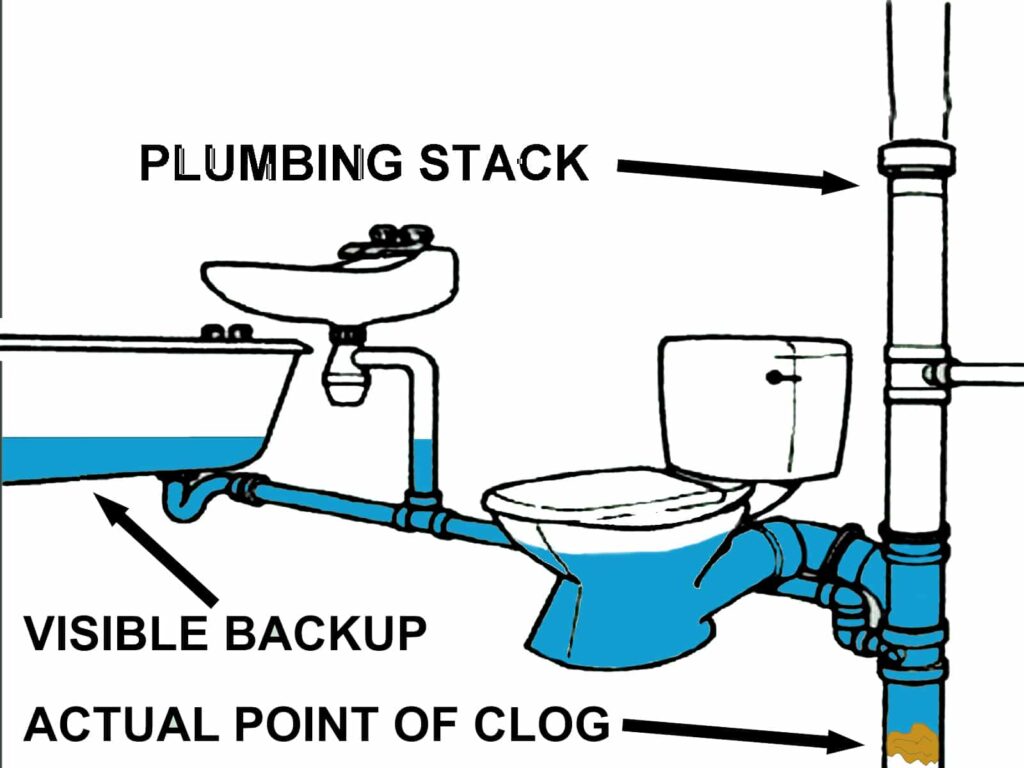
A plumbing stack is an essential component of a plumbing system that plays a crucial role in the proper functioning and maintenance of a building. It is responsible for removing waste and wastewater from the various fixtures and appliances in a structure. Without a plumbing stack, the plumbing system would be ineffective and inefficient, leading to plumbing issues and potential health hazards.
The plumbing stack serves as a vertical pipe that runs through multiple floors of a building, connecting the drainage pipes of different levels. It ensures the smooth flow of waste materials downward and out of the building, preventing clogs and blockages. Additionally, the plumbing stack also provides ventilation for the drainage system, allowing gases to escape and maintaining the proper air pressure within the pipes. This helps prevent odors, backflow, and potential damage to the plumbing system. Proper installation and maintenance of plumbing stacks are crucial to the overall functionality and efficiency of a building’s plumbing system.
A plumbing stack, also known as a soil stack or waste stack, is a vertical pipe that runs through a building and connects to the main sewer line. Its primary function is to carry waste and wastewater from various plumbing fixtures, such as toilets, sinks, and showers, to the sewer system. The plumbing stack is typically made of durable materials like cast iron or PVC and is essential for proper drainage and ventilation in a building. It plays a crucial role in maintaining the overall plumbing system’s functionality and preventing clogs and sewer gas buildup.
Understanding Plumbing Stacks: A Key Component in Plumbing Systems
A plumbing stack is an essential part of any plumbing system. It plays a vital role in maintaining the proper flow of water and waste materials in a building. Understanding what a plumbing stack is and how it functions is crucial for homeowners, plumbers, and anyone involved in the construction or maintenance of a building.
What is a Plumbing Stack?
A plumbing stack, also known as a soil stack or waste stack, is a vertical pipe that provides a pathway for wastewater and sewage to flow out of a building and into the sewer or septic system. It is typically made of cast iron, PVC, or ABS plastic and is connected to the building’s drainage system.
The plumbing stack extends from the building’s lowest level (basement or crawl space) to the roof. It acts as a central hub for all the plumbing fixtures in the building, allowing wastewater from sinks, toilets, showers, and other fixtures to be efficiently discharged.
In addition to carrying wastewater, the plumbing stack also serves as a venting system. It allows air to enter the pipes, preventing the formation of a vacuum that could impede the flow of water. Venting also helps to reduce the buildup of unpleasant odors by allowing gases to escape safely.
Plumbing stacks are typically designed and installed by professional plumbers to meet local building codes and regulations. These codes ensure that the plumbing system operates effectively and safely, protecting both the occupants of the building and the environment.
Components of a Plumbing Stack
A plumbing stack consists of several key components that work together to facilitate the flow of water and waste. These components include:
- Main Stack: The main vertical pipe that extends from the lowest level of the building to the roof. It connects all the horizontal drain lines from the plumbing fixtures and carries wastewater and sewage.
- Branch Stacks: These are secondary vertical pipes that connect the plumbing fixtures to the main stack. Each branch stack serves a portion of the building and connects to the main stack at a higher level.
- Vent Stacks: Vent stacks are vertical pipes that allow air to enter the plumbing system, preventing pressure differentials and ensuring smooth drainage. These pipes extend above the roof and act as vents for the plumbing system.
- Stack Vents: Stack vents are horizontal pipes that connect multiple vent stacks within a building. They help to equalize pressure and improve the overall performance of the plumbing system.
- Sanitary Tees and Wyes: These components connect the branch lines to the main stack, allowing wastewater to flow from the fixtures into the stack. Sanitary tees have a vertical inlet, while wyes have a diagonal inlet.
How Does a Plumbing Stack Work?
A plumbing stack works through a combination of gravity and pressure differentials. As water and waste flow down the drain from a plumbing fixture, they enter the branch line and then the main stack. The force of gravity helps to move the wastewater downward.
Simultaneously, air is drawn into the plumbing system through vent stacks or stack vents. This prevents the formation of a vacuum and maintains the pressure equilibrium within the system. The presence of air also prevents the escape of odorous gases into the building.
Once the wastewater reaches the main stack, it continues to flow downward until it reaches the sewer or septic system. The vertical design of the stack allows for efficient drainage and minimizes the risk of clogs or backups.
Types of Plumbing Stacks
There are two main types of plumbing stacks commonly found in buildings:
1. Wet Stacks: Wet stacks are primarily used in high-rise buildings or multi-story structures. In wet stacks, the drainage and venting functions are combined within the same pipe. Water and waste flow down one side of the stack, while air is drawn in on the other side.
2. Dry Stacks: Dry stacks are more commonly found in residential buildings. Unlike wet stacks, dry stacks have separate pipes for drainage and venting. The plumbing fixtures are connected to the drainage system, while vent pipes provide the necessary air circulation.
The choice between wet and dry stacks depends on the specific building requirements and local plumbing codes.
Maintaining and Troubleshooting Plumbing Stacks
Proper maintenance and regular inspections are essential for the optimal performance of plumbing stacks. Here are a few tips for maintaining and troubleshooting plumbing stacks:
1. Regular Inspections
Periodically inspect the plumbing stack for signs of wear, leaks, or blockages. It’s crucial to catch any issues early to prevent further damage and expensive repairs.
2. Clearing Blockages
If you experience slow drainage or backup in your plumbing fixtures, it may indicate a blockage in the plumbing stack. Use a plunger, plumbing snake, or call a professional plumber to clear the blockage.
3. Ventilation Problems
If you notice foul odors or gurgling sounds coming from your drains, it could indicate a ventilation problem in the plumbing stack. A blocked vent can lead to slow drainage and a malfunctioning plumbing system. A professional plumber can evaluate and correct any ventilation issues.
Conclusion
A plumbing stack is a crucial component of any plumbing system, providing a pathway for wastewater and sewage to exit a building. Understanding the different parts and functions of a plumbing stack is essential for homeowners and professionals involved in plumbing design or maintenance. By ensuring proper maintenance and timely repairs, plumbing stacks can continue to operate efficiently and effectively for years to come.
Understanding Plumbing Stacks
In the world of plumbing, a plumbing stack is an essential component of most buildings’ plumbing systems. It serves as the main vertical pipe that carries wastewater and sewage from different floors to the main sewer line. This vertical pipe is typically located near the center of the building, running from the foundation to the roof.
The plumbing stack plays a crucial role in maintaining proper waste disposal in the building. It ensures the flow of wastewater from toilets, showers, sinks, and other plumbing fixtures to the sewer system. Additionally, it also allows ventilation, preventing the build-up of harmful gases or odors within the building.
Plumbing stacks are usually made of durable materials like cast iron or PVC, depending on the building’s age and local plumbing codes. They are designed to handle the weight and force of the wastewater flowing through them. Regular maintenance and inspections are necessary to identify any potential issues and ensure the stack’s proper functioning.
Without a properly functioning plumbing stack, a building’s plumbing system can experience blockages, leaks, and unpleasant odors. It is crucial to hire a professional plumber to handle any repairs or maintenance needs related to the plumbing stack to ensure the efficient and safe operation of the building’s plumbing system.
Key Takeaways – What Is A Plumbing Stack?
- A plumbing stack is a vertical pipe that extends from the main sewer line to the roof of a building.
- It is an essential part of a plumbing system, as it allows waste and wastewater to flow out of the building.
- The plumbing stack is typically made of cast iron or PVC pipe, and it is designed to withstand the pressure and weight of the water and waste.
- The size of the plumbing stack depends on the number of fixtures in the building and the flow rate of the wastewater.
- Maintenance of the plumbing stack is important to prevent clogs and leaks, which can cause damage to the building and the plumbing system.
Frequently Asked Questions
In this section, we provide answers to some commonly asked questions about plumbing stacks.
1. What is the purpose of a plumbing stack?
A plumbing stack, also known as a soil stack or waste stack, is a vertical pipe that connects the plumbing fixtures in a building to the sewer system or septic tank. Its main purpose is to carry wastewater and sewage away from the building and dispose of it in a safe and sanitary manner.
The plumbing stack also serves as a vent pipe, allowing air to enter the drainage system. This helps maintain proper pressure and prevents trap siphoning, which can lead to sewer gas odors and reduced drainage efficiency.
2. How does a plumbing stack work?
A plumbing stack works by utilizing gravity to transport wastewater and sewage from the plumbing fixtures to the main sewer line or septic tank. When a fixture is used, such as a toilet or sink, the wastewater flows into the plumbing stack and is carried down by the force of gravity.
As the wastewater travels down the plumbing stack, it combines with other wastes from the building’s plumbing system. This mixture continues flowing downward through the stack until it reaches the main sewer line or septic tank, where it is ultimately disposed of.
3. How does a plumbing stack differ from a vent stack?
A plumbing stack, as mentioned earlier, serves both as a drainage pipe and a vent pipe. It carries wastewater down to the sewer system and also allows air to enter the drainage system.
A vent stack, on the other hand, is solely dedicated to providing ventilation for the plumbing system. It allows odors and gases to escape from the drainage system and prevents the suction of water from traps.
4. What materials are commonly used for plumbing stacks?
Plumbing stacks can be made from various materials, depending on the building’s plumbing system requirements and local plumbing codes. Some common materials used for plumbing stacks include cast iron, PVC (polyvinyl chloride), and ABS (acrylonitrile butadiene styrene).
Cast iron is a durable and long-lasting material that has been used for plumbing stacks for many years. PVC and ABS, on the other hand, are more popular in modern plumbing systems due to their cost-effectiveness and ease of installation. The specific material used will depend on factors such as budget, local codes, and the type of building.
5. Can plumbing stacks become clogged?
Yes, plumbing stacks can become clogged over time due to the accumulation of debris, such as hair, food particles, grease, and mineral deposits. These clogs can restrict the flow of wastewater and sewage, leading to slow draining fixtures, backups, and foul odors.
To prevent clogs in plumbing stacks, regular maintenance and cleaning are recommended. This may include using drain cleaners, snaking the stack to remove obstructions, or even replacing old pipes if necessary. It is important to address clogs promptly to avoid more significant plumbing issues.
Plumbing Rough In – What is a Plumbing Stack (EP8) – 2023
In conclusion, a plumbing stack is a vertical pipe that runs through a building, connecting all the plumbing fixtures to the main sewer line. It is an essential part of the plumbing system as it allows waste water and gases to flow out of the building safely and efficiently.
The plumbing stack is typically made of durable materials such as cast iron or PVC, and it is designed to withstand the pressures and demands of a building’s plumbing system. It plays a crucial role in maintaining proper drainage and preventing plumbing emergencies such as clogs and leaks.